






Hassle free, 2-Year Warranty
Fast, Free Shipping on Orders $35+
Lifetime Technical Support
30-Day Money Back Guarantee
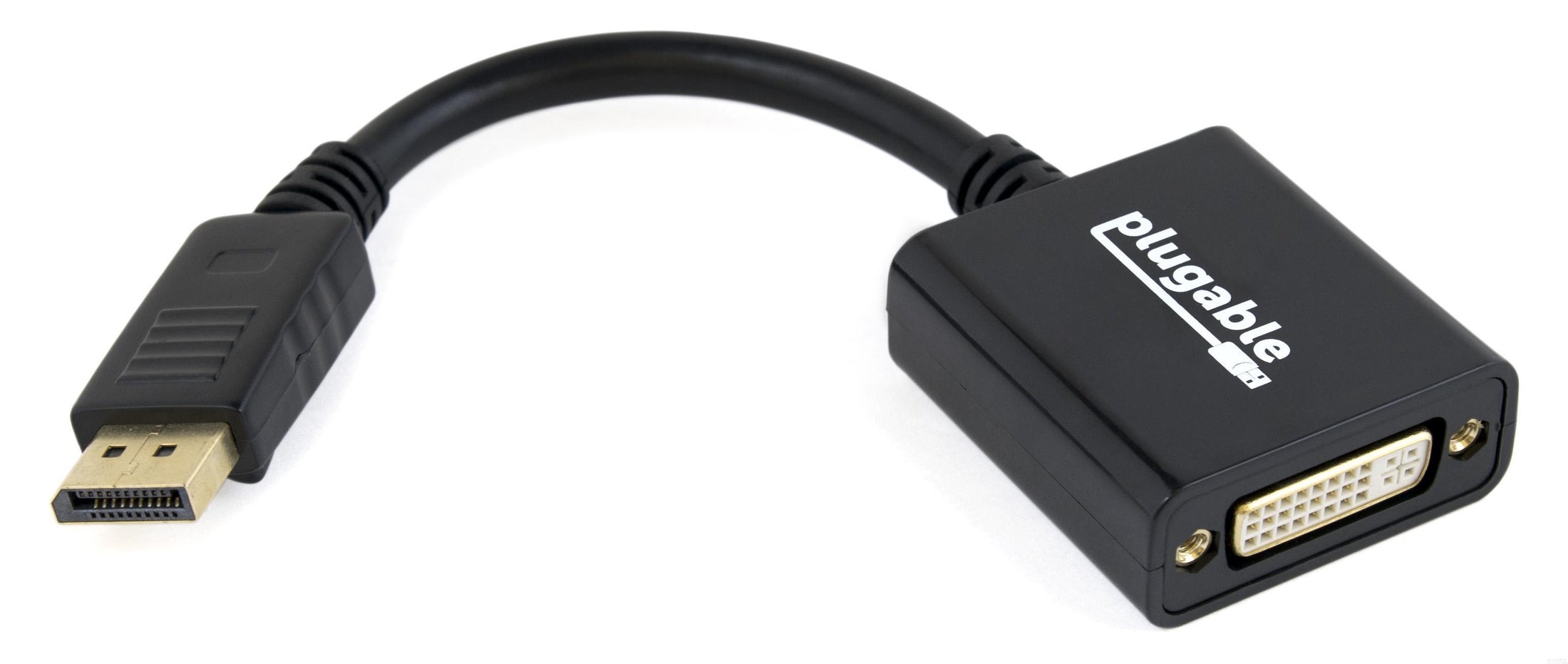
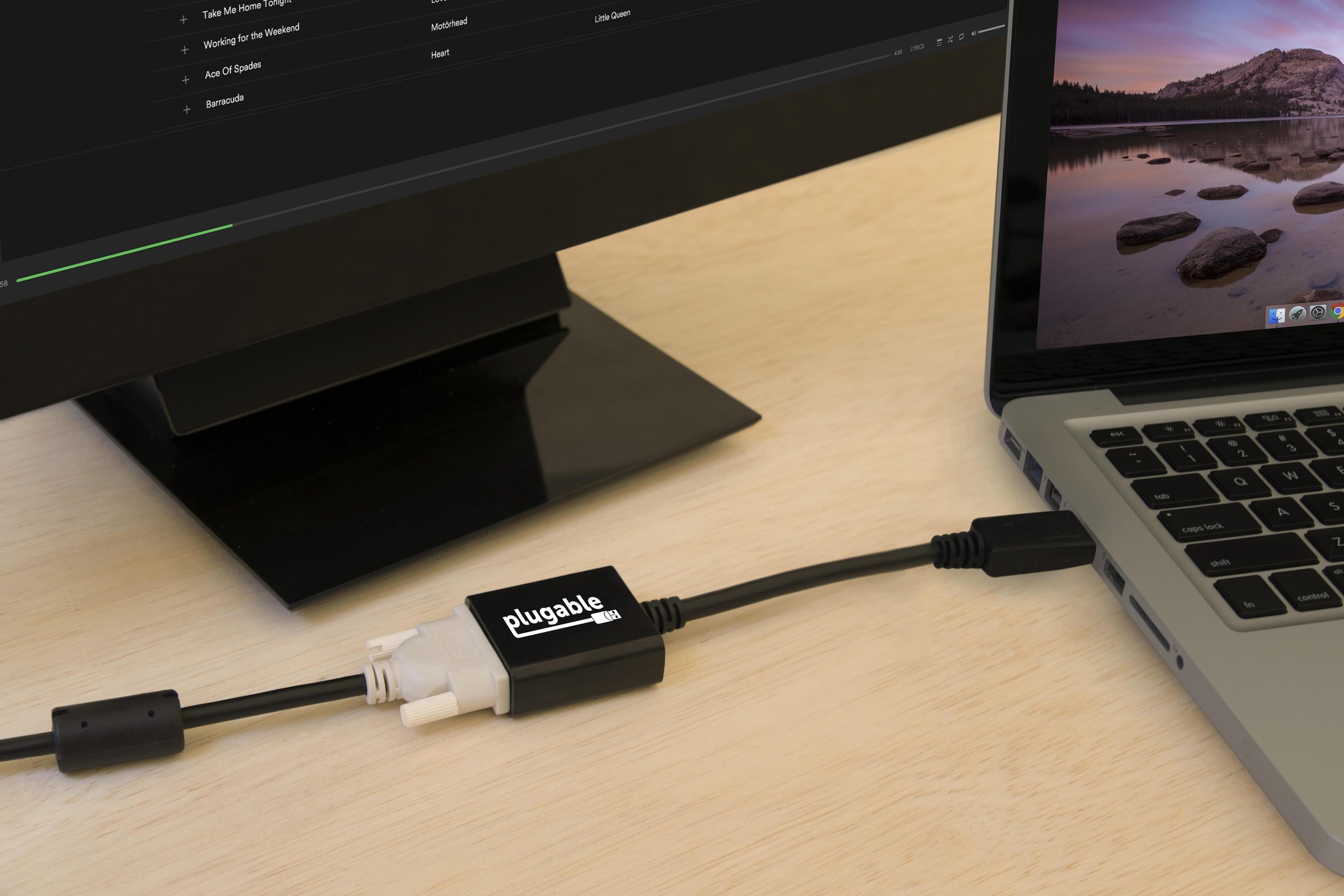
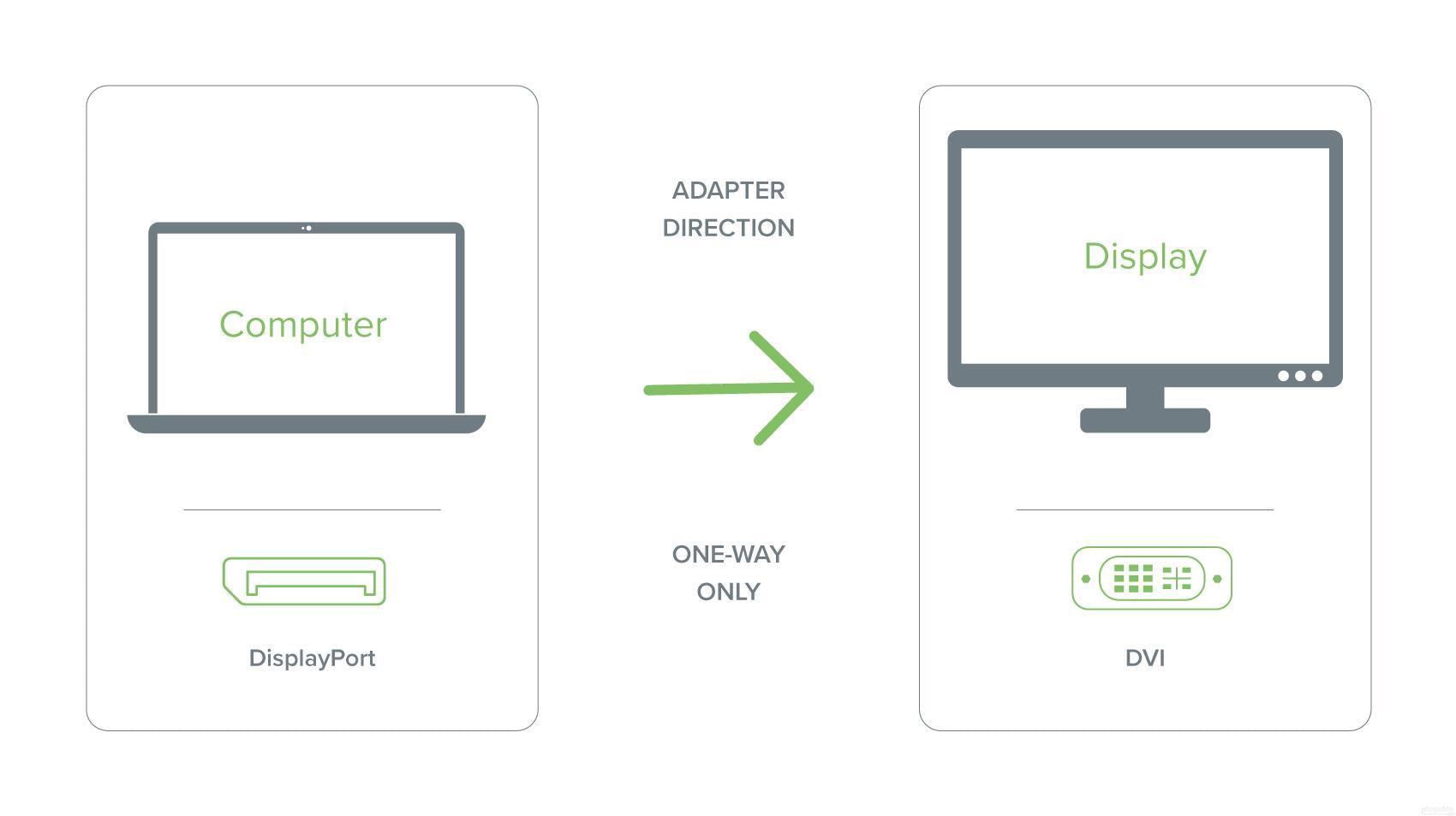
Plugable DisplayPort to DVI Adapter (Passive)
$8.95 USD
SKU: DPM-DVIFAmazon Rating : (49 Reviews)
Features
- DP to DVI— Converts full size DisplayPort (Dual-Mode/DP++) output on your laptop or desktop to a DVI output to enable connection to a DVI monitor
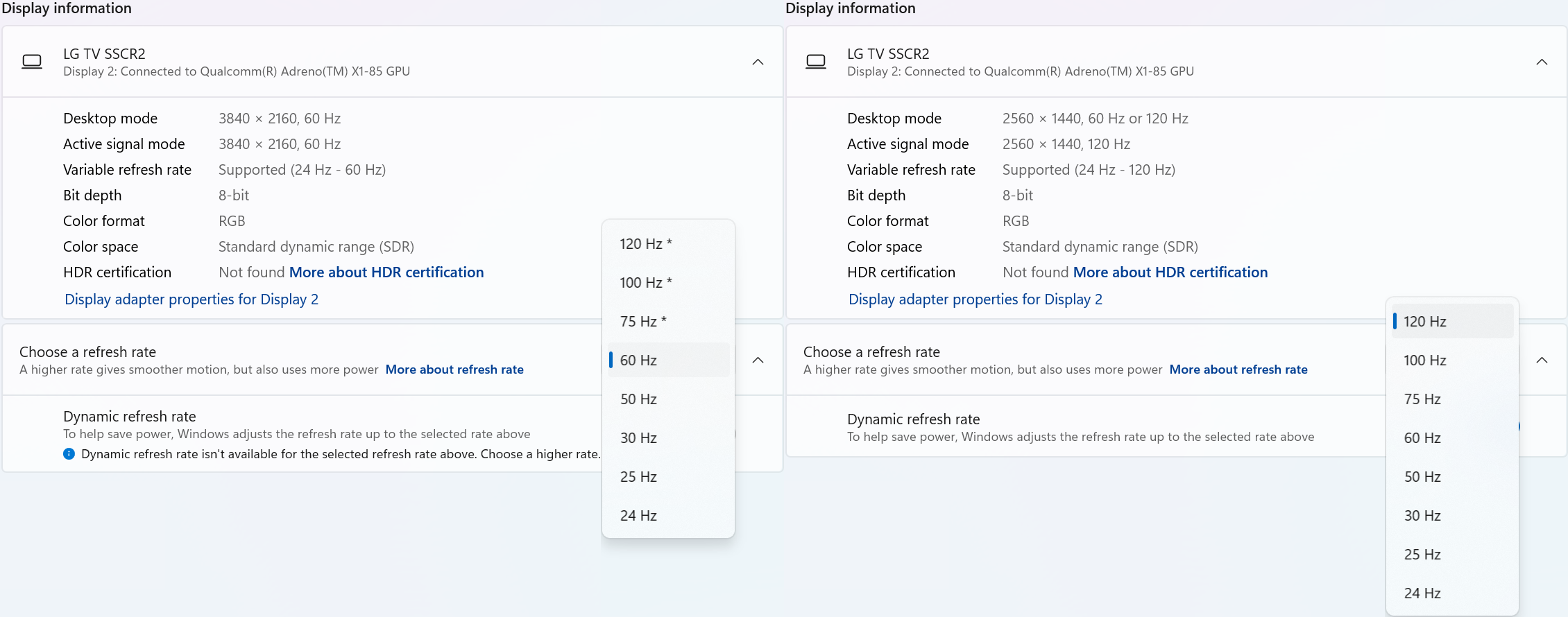
- Supported Resolutions— Supports DVI displays up to 1920x1200 displays at 60Hz refresh rate
- Simple Installation— No installation software or drivers required; just plug and play
- Compatibility— Passive adapter is compatible with Dual-Mode DisplayPort (DP++) output ports only. Not a bidirectional adapter. Please note that the host system's graphics processor and the connected DVI display need to support the desired resolution
- 2-Year Coverage, Lifetime Support— Every Plugable product, including this displayport to DVI adapter, is covered against defects for 2 years and comes with lifetime support. If you ever have questions, contact our North American-based team - even before purchase